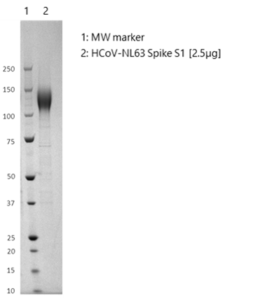
Human Coronavirus NL63 Spike Glycoprotein (S1), His-Tag (HEK293)
Price range: $794.58 through $2,987.02 excl. VAT
Human coronavirus NL63 spike glycoprotein is a recombinant HCoV-NL63 spike subunit 1 protein (S1), with C-terminus His-tag. This antigen is manufactured in HEK293 cells, with
HUMAN CORONAVIRUS NL63 SPIKE GLYCOPROTEIN (S1), HIS-TAG (HEK293)
Human coronavirus NL63 spike glycoprotein is a recombinant HCoV-NL63 spike subunit 1 protein (S1), with C-terminus His-tag.
PRODUCT DETAILS – HUMAN CORONAVIRUS NL63 SPIKE GLYCOPROTEIN (S1)
-
- Human coronavirus NL63 spike Glycoprotein (S1), corresponding to amino acids 1-713 (NCBI: QEG03748.1; sequence strain: HCoV_NL63/Seattle/USA/SC0768/2019).
- Protein contains a C-terminal His-tag with apparent molecular weight of 120 kDa.
- Protein was produced in HEK293 cells and purified from culture supernatant by immobilized metal affinity chromatography, followed by dialysis.
- Presented as liquid, Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline pH7.4, sterile filtered.
BACKGROUND
Coronaviruses (CoV) are enveloped, positive stranded RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales, family Coronaviridae, subfamily Coronavirinae. The subfamily Coronavirinae contains the four genera Alpha-, Beta-, Gamma-, and Deltacoronavirus. Alpha- and betacoronaviruses mainly infect humans (Corman et al, 2018). The alphacoronavirus HCoV-NL63 was first isolated in 2003 from a 7-month-old child suffering from bronchiolitis and conjunctivitis (van der Hoek et al., 2004). Bat-CoVs have been identified which are related to HCoV-NL63. The genome organization of the NL63-related bat CoVs are similar to that of HCoV-NL63 (ORF1ab-S-ORF3-E-M-N) with the exception that the bat CoV genomes encode an additional open reading frame (ORF X) downstream of the N gene (Tao et al., 2017). However, the zoonotic sources of HCoV-NL63 are unknown. It is thought that HCoV-NL63 may have diverged from a HCoV-229E ancestor in the past, followed by a separation into two distinct HCoV-NL63 lineages. There is also evidence of recombination between viral isolates during the evolution of HCoV-NL63, resulting in a mosaic genome structure (Pyrc et al., 2006).
HCoV-NL63 has a single-stranded RNA genome (27,553 bp) which encodes for a 5′ replicase polyprotein (ORF1a and ORF1b) which encode for the enzymes required for viral RNA replication. The genome also encodes for the 3′ structural proteins, including spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M) and nucleocapsid (N), which are common to all coronaviruses. The structural proteins are involved in various viral processes, including virus particle formation (Pyrc et al., 2004). Coronavirus spike proteins mediate attachment to the cellular receptors and subsequent fusion of the virus and cell membrane. The N-terminal portion of HCoV-NL63 spike protein contains a unique 179 amino acid domain not present in other coronaviruses. This region represents the most variable region of the HCoV-NL63 genome and a role in immune evasion for this region has been proposed (Pyrc et al., 2007). HCoV-NL63 uses receptor angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)-2 for entry into the host cell. There has been a high occurrence of co-infections reported with HCoV-NL63 and other respiratory viruses, including other human coronaviruses, influenza A virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), parainfluenza virus and human metapneumovirus (hMPV), resulting in increased severity of symptoms and increased opportunities for recombination (Abdul-Rasool & Fielding, 2010).
REFERENCES
- Abdul-Rasool S, Fielding, BC. Understanding Human Coronavirus HCoV-NL63. Open Virol J. 2010; 4: 76–84.
- Corman VM, Muth D, Niemeyer D, Drosten C. Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 2018;100:163-188.
- Hamre D, Procknow JJ. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966;121(1):190-193.
- Pyrc K, Jebbink MF, Berkhout B, van der Hoek L. Genome structure and transcriptional regulation of human coronavirus NL63. Virol J. 2004;1:7.
- Pyrc K, Dijkman R, Deng L, et al. Mosaic structure of human coronavirus NL63, one thousand years of evolution. J Mol Biol. 2006;364(5):964-973.
- Pyrc K, Berkhout B, van der Hoek L. The novel human coronaviruses NL63 and HKU1. J Virol. 2007;81(7):3051-3057.
- Tao Y, Shi M, Chommanard C, et al. Surveillance of Bat Coronaviruses in Kenya Identifies Relatives of Human Coronaviruses NL63 and 229E and Their Recombination History. J Virol. 2017;91(5):e01953-16.
- van der Hoek L, Pyrc K, Jebbink MF, et al. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat Med. 2004;10(4):368-373.