Human anti-Rubella virus IgG (DD5), Recombinant
Price range: $346.02 through $1,474.57 excl. VAT
Human anti-Rubella Virus IgG kappa, clone DD5 is a recombinant monoclonal antibody expressed in HEK293 cells, generated using Rubella VLP (REC32047) as the immunogen.
Human anti-Rubella virus IgG (DD5), Recombinant
Human anti-Rubella Virus IgG kappa, clone DD5 is a recombinant monoclonal antibody expressed in HEK293 cells, generated using Rubella VLP (REC32047) as the immunogen. The Native Antigen Company also supplies additional recombinant IgM antibody, the Human chimeric anti-Rubella Virus IgM (clone DD5, MAB12519), expanding the range of antibodies available for rubella diagnostics and assay development.
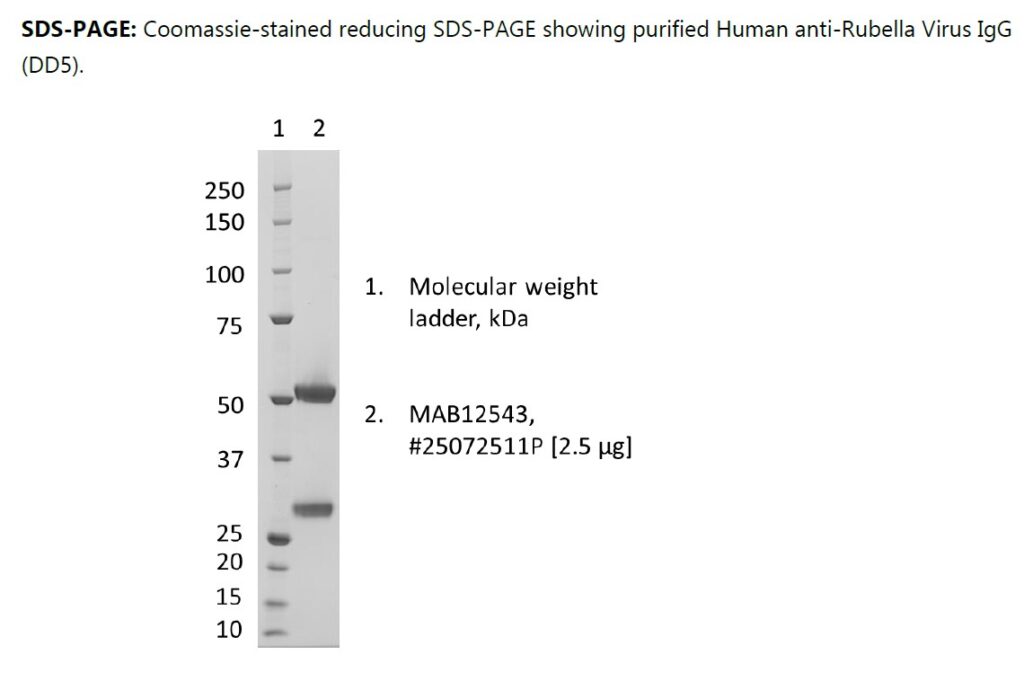
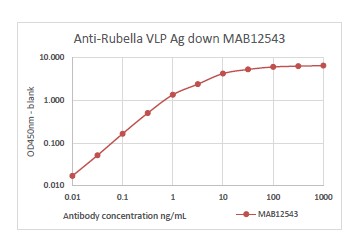
PRODUCT DETAILS – Human anti-Rubella virus IgG (DD5), Recombinant
- Isotype: human IgG kappa
- Rubella virus-like particles were used as immunogen.
- Presented as Liquid in DPBS Buffer.
BACKGROUND
Rubella is a mild viral infection that healthy individuals typically clear without significant complications. However, it poses a serious risk during early pregnancy, as it can cause congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) in the fetus, leading to severe birth defects. Accurate IgG serology testing is essential to assess an individual’s immunity status, monitor population-level protection, and guide prenatal care and public health surveillance efforts (Dimech et al., 2015).
Recombinant Rubella IgG is produced using recombinant DNA technology. Compared to traditional polyclonal antibodies derived from serum, recombinant IgG offers several advantages, including sequence-defined specificity, batch-to-batch consistency, and high purity. This ensures their reproducible performance in diagnostic settings (Frenzel et al., 2013; Haralambieva et al., 2017).
In practice, recombinant Rubella IgG is used as a control, calibrator, or assay reagent for rubella IgG detection platforms, such as ELISAs, which are used for immunity screening and vaccine program evaluation (Haralambieva et al., 2017). Given the documented concern over inconsistent quantitative results across different assays, even those calibrated to the WHO international standard, defining and standardizing reagents like recombinant antibodies is crucial for reliable rubella immunity testing, assay validation, and serological surveillance (Dimech et al., 2013; Dimech et al., 2015)
REFERENCES
Dimech, W. et al. (2015). Standardization of assays that detect anti-rubella virus IgG antibodies. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 53(1), 164–170.
Haralambieva, I. H. et al. (2017). Characterization of rubella-specific humoral immunity following two doses of MMR vaccine using proteome microarray technology. PLOS ONE, 12(1), e0169416.
Frenzel, A. et al. (2013). Expression of recombinant antibodies: diagnostic applications. Frontiers in Immunology, 4, 217.
Dimech, W. et al. (2013). Investigation into low-level anti-rubella IgG results reported by commercial immunoassays. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 20(8), 1251–1255.