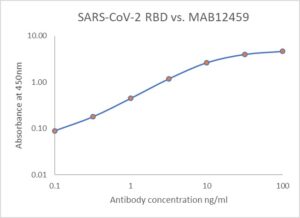
ELISA: Antigen-down ELISA showing binding of MAB12459 to immobilized SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD protein (REC31882).
Human IgG1 Anti SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S1) RBD Antibody (DH6)
Price range: $618.01 through $2,163.01 excl. VAT
Recombinant humanized version of the neutralizing mouse monoclonal antibody MAB12444. Antibody is specific for SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD). The original monoclonal antibody (MAB12444) is neutralizing against SARS-CoV-2, but not against SARS-CoV-1 or MERS-CoV. This antibody has been manufactured for use in ELISA immunoassay development.
HUMAN IgG1 ANTI-SARS-COV-2 SPIKE (S1) RBD ANTIBODY (DH6)
Recombinant humanized version of the neutralizing mouse monoclonal antibody MAB12444. Antibody is specific for SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD). This antibody has been manufactured for use in ELISA immunoassay development.
PRODUCT DETAILS – HUMAN IgG1 ANTI-SARS-COV-2 SPIKE (S1) RBD ANTIBODY (DH6)
- Recombinant humanized antibody, which is specific for SARS-CoV-2 RBD.
- The original monoclonal antibody (MAB12444) is specific for the spike receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2, recognizing RBD from Wuhan-Hu-1, UK (Alpha), South African (Beta) Brazilian (Gamma) and Indian Kerala variants. No cross-reactivity observed in ELISA with SARS-CoV-2 subunit 2 (S2) or spike subunit 1 (S1) proteins from SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-229E and HCoV-HKU1.
- The original monoclonal antibody (MAB12444) is neutralizing against SARS-CoV-2, but not against SARS-CoV-1 or MERS-CoV.
- The original monoclonal antibody (MAB12444) is suitable for use as capture or detection antibody in ELISA assays. Capture antibody with MAB12446 as detection antibody. Detection antibody with MAB12422 or MAB12446 as capture antibody.
- Immunogen was SARS-CoV-2 RBD (REC31882, aa 1-223) expressed in HEK293 cells.
BACKGROUND
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent of the coronavirus induced disease 19 (COVID-19) which emerged in China in late 2019, resulting in a worldwide epidemic (Zhou et al., 2020). SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus with a number of important structural proteins, including the envelope (E) protein, the membrane (M) protein, the spike (S) protein, and the nucleoprotein (N). The S protein assists in the attachment of the virus to the human cell and comprises intracellular, transmembrane, and extracellular regions. The extracellular region contains the S1 receptor binding subunit (RBD) and the S2 membrane fusion subunit. Generally, following SARS-CoV-2 infection, antibodies appear after 7–14 days and persist for weeks after viral clearance. The most commonly detected antibodies are against the N protein and the S protein. Coronavirus neutralizing antibodies primarily target the trimeric spike (S) glycoproteins on the viral surface (Wang et al., 2020) and can change the course of infection in an infected individual by supporting virus clearance or protecting an uninfected host that is exposed to the virus (Prabakaran et al., 2009). However, the antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 remain poorly understood (Tang et al., 2020) and better understanding of how the viral coating triggers a healthy immune system’s recognition and neutralisation of the virus is critical for optimisation of diagnostic tests (Petherick, 2020). It has been suggested that spike RBD may be a better target than N for diagnostic tests (Rosadas et al., 2020). The Native Antigens monoclonal antibodies, which are specific for SARS-CoV-2, have been manufactured to meet the need for improved COVID-19 diagnostic assays.
REFERENCES
- Petherick A. Developing antibody tests for SARS-CoV-2. Lancet. 2020 Apr 4;395(10230):1101-1102.
- Prabakaran P, Zhu Z, Xiao X, Biragyn A, Dimitrov AS, Broder CC, Dimitrov DS. Potent human monoclonal antibodies against SARS CoV, Nipah and Hendra viruses. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009 Mar;9(3):355-68.
- Rosadas C, Randell P, Khan M, McClure MO, Tedder RS. Testing for responses to the wrong SARS-CoV-2 antigen? Lancet. 2020 Sep 5;396(10252):e23.
- Tang YW, Schmitz JE, Persing DH, Stratton CW. Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19: Current Issues and Challenges. J Clin Microbiol. 2020 May 26;58(6):e00512-20.
- Wang C, Li W, Drabek D, Okba NMA, van Haperen R, Osterhaus ADME, van Kuppeveld FJM, Haagmans BL, Grosveld F, Bosch BJ. A human monoclonal antibody blocking SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Commun. 2020 May 4;11(1):2251.
- Zalzala HH. Diagnosis of COVID-19: Facts and challenges. New Microbes New Infect. 2020 Sep 16:100761.
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang RD, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Zheng XS, Zhao K, Chen QJ, Deng F, Liu LL, Yan B, Zhan FX, Wang YY, Xiao GF, Shi ZL. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020 Mar;579(7798):270-273.
You may also like…
Mouse Anti SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S1) Antibody (HH10)
Price range: $737.83 through $2,215.56 excl. VAT
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein (S1) RBD, His-Tag (HEK293)
Price range: $691.59 through $2,635.97 excl. VAT
Human IgG1 Anti SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S1) Antibody (EB5)
Price range: $618.01 through $2,163.01 excl. VAT
