Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) B Glycoprotein G, His-Tag (HEK293)
$557.05 – $1,961.22Price range: $557.05 through $1,961.22 excl. VAT
Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) B glycoprotein G is a recombinant antigen produced in mammalian cells to Glycoprotein G attaches the virion to the host cell membrane by interacting with glycosaminoglycans, initiating the infection. It also interacts with host DDX58 and inhibits DDX58-mediated signaling pathway in order to prevent the establishment of the antiviral state.
HUMAN METAPNEUMOVIRUS (HMPV) B GLYCOPROTEIN G, HIS-TAG (HEK293)
Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) B glycoprotein G is a recombinant antigen produced in mammalian cells to high purity. Glycoprotein G attaches the virion to the host cell membrane by interacting with glycosaminoglycans, initiating the infection. It also interacts with host DDX58 and inhibits DDX58-mediated signaling pathway in order to prevent the establishment of the antiviral state.
PRODUCT DETAILS – HUMAN METAPNEUMOVIRUS (HMPV) B GLYCOPROTEIN G, HIS-TAG (HEK293)
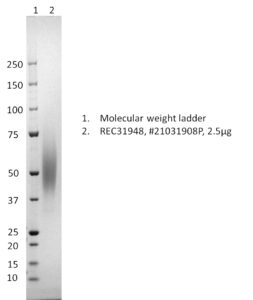
- Recombinant hMPV B Glycoprotein G.
- Produced in HEK293 cells and purified from culture supernatant.
- IMAC followed by anion exchange and dialysis.
- Presented in PBS at
BACKGROUND
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is an enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus Metapneumoviridae, of the family Pneumoviridae. hPMV is closely related to Respiratory Syncytial virus (RSV), which belongs to the genus Orthopneumovirus within the same family (Alfonso et al., 2016). Human metapneumovirus is globally widespread and spreads seasonally in temperate climates. Genomic analysis has shown that hMPV exists as two genotypes (A and B), which are further divided into the subgroups A1, A2, B1 and B2. Each subgroup has a distinct geographical distribution but can circulate separately or concurrently (Boivin et al., 2004). Transmission of HPMV from person-to-person predominantly occurs through contact with airborne droplets from an infected individual, produced by coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread through contact with contaminated hands or surfaces. Serosurveillance studies have shown that most children worldwide are infected with hMPV by the age of 5 (Shafagati et al., 2018). Rates of hospitalization of children for hMPV infection are highest in the first year of life but continue to occur throughout early childhood. Studies have tended to suggest that the peak age of hospitalization for hMPV is between 6 and 12 months of age, which is later than the peak age of hospitalization for RSV (2–3 months).
REFERENCES
- Afonso CL, Amarasinghe GK, Bányai K, et al. Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: update 2016. Arch Virol. 2016;161(8):2351-2360.
- Boivin G, Mackay I, Sloots TP, et al. Global genetic diversity of human metapneumovirus fusion gene. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(6):1154-1157.
- Shafagati N, Williams J. Human metapneumovirus – what we know now. F1000Res. 2018;7:135.