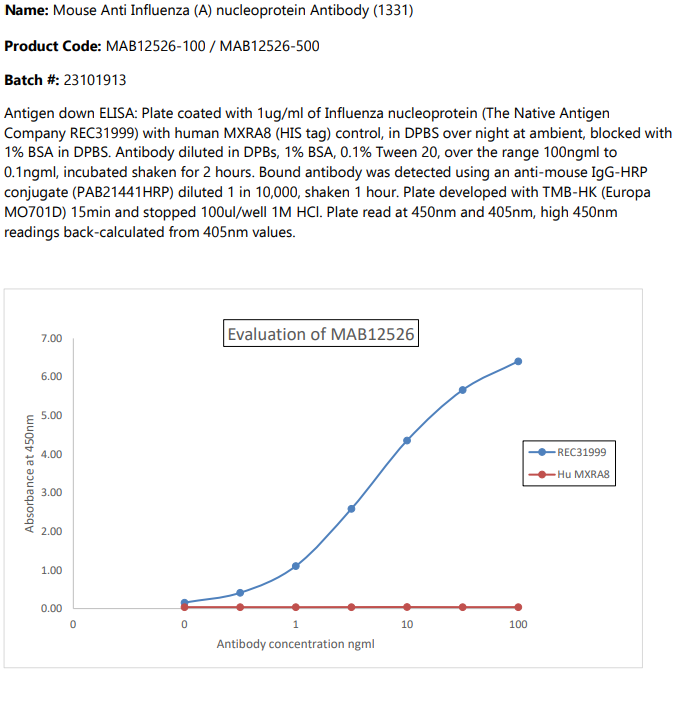
Mouse Anti Influenza (A) nucleoprotein Antibody (1331)
Price range: $420.41 through $1,054.91 excl. VAT
Influenza A virus nucleoprotein antibody is a monoclonal antibody made in mouse and suitable for the detection of Influenza A virus nucleoprotein. Antibody is suitable for WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA. Broadly reactive clone, showing reactivity to over 70 tested strains of Human, Swine, Avian and Equine Influenza A nucleoprotein.
Mouse Anti Influenza (A) nucleoprotein Antibody (1331)
Influenza A virus nucleoprotein antibody is a monoclonal antibody made in mouse and suitable for the detection of Influenza A virus nucleoprotein. Broadly reactive clone, showing reactivity to over 70 tested strains of Human, Swine, Avian and Equine Influenza A nucleoprotein.
PRODUCT DETAILS – Mouse Anti Influenza (A) nucleoprotein Antibody (1331)
- Mouse anti-Influenza A nucleoprotein monoclonal antibody (clone 1331)
- Suitable for WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA
- Presented as Liquid.
BACKGROUND
Influenza viruses are enveloped, segmented, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses of the Orthomyxoviridae family. There are three genera of influenza virus that are clinically relevant to humans, these are influenza A, B and C. Influenza A and B virus genomes each comprise eight negative-sense, single-stranded viral RNA (vRNA) segments, while influenza C virus has a seven-segment genome. Influenza A viruses circulate worldwide are the most virulent human pathogens among the three influenza types and are the predominant cause of seasonal and pandemic influenza (Bouvier, NM). Influenza B viruses also circulate worldwide and cause seasonal influenza in temperate climates. However, Influenza B viruses are more stable than Influenza A viruses, and are grouped into two lineages B/Yamagata and B/Victoria (CDC).
One of the three core Influenza polypeptides is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and a single-strand RNA (ssRNA) binding protein, often referred to as a nucleoprotein (NP). NP encapsidates the virus genome to form a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) particle for the purposes of transcription and packaging. NP is not just the structural component of the virus transcription machinery but performs multiple essential functions throughout the virus life cycle (Portela & Digard, 2002). Influenza A virus RNA segment 5 encodes NP is a polypeptide of 498 amino acids in length; in influenza B and C viruses, the length of the homologous NP polypeptide is 560 and 565 residues, respectively (Londo et al., 1983; Nakada et al., 1984).
REFERENCES
- Bouvier, N.M. and Palese, P. (2008). The Biology of Influenza viruses. Vaccine.26(Suppl 4): D49–D53.
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention: Influenza type A viruses.
- Londo DR, Davis AR, Nayak DP. Complete nucleotide sequence of the nucleoprotein gene of influenza B virus. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):642-8.
- Nakada S, Creager RS, Krystal M, Palese P. Complete nucleotide sequence of the influenza C/California/78 virus nucleoprotein gene. Virus Res. 1984 Sep;1(6):433-41.
- Portela A, Digard P. The influenza virus nucleoprotein: a multifunctional RNA-binding protein pivotal to virus replication. J Gen Virol. 2002 Apr;83(Pt 4):723-734.