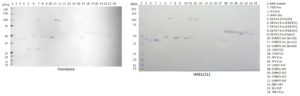
Western Blot: 100ng of each antigen was used for SDS-PAGE, in non-reduced form. Proteins were transferred using Transblot for 7 minutes at 25V. 5% dry milk in PBS-T was used as blocking buffer and dilution buffer for antibodies. Primary antibodies are given below, and goat anti-mouse-IgG-HRP secondary antibody (Biorad 103005) was used at 1:1000. All steps were carried out for 1h at room temperature with gentle rocking. KPL Membrane TMB was used for detection. Development time 30 seconds.
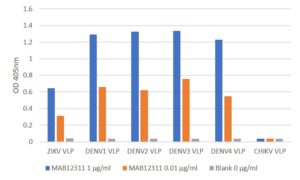
ELISA: antigen down ELISA using Zika virus VLPs. Antibody also recognises Dengue virus and Chikungunya virus VLPs.
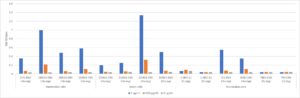
ELISA: antibody recognises Zika virus envelope protein and envelope proteins from Dengue virus (produced in insect and mammalian cells), Japanese Encephalitis virus and West Nile virus.
MOUSE ANTI-ZIKA VIRUS VLP/ENV ANTIBODY (IG3)
This mouse anti Zika virus VLP antibody recognises the Zika virus VLP comprising Envelope, Pre-membrane and Membrane proteins of Zika virus.
PRODUCT DETAILS – MOUSE ANTI-ZIKA VIRUS VLP/ENV ANTIBODY (IG3)
- Anti Zika VLP antibody (isotype IgG1 kappa) recognizes the Zika virus VLP comprising Envelope, Pre-membrane and Membrane proteins.
- Antibody also recognises Envelope proteins from Dengue virus, Japanese Encephalitis virus and West Nile virus in ELISA assay.
- Suitable for use in direct ELISA and Western blot (non-reduced).
BACKGROUND
Zika virus is an emerging disease that is spread by Aedes mosquitoes. The virus was first isolated in Central Africa, and has since spread to South Asia and more recently to South America. It is a member of the flavivirus family, and is structurally closely related to viruses such as Dengue Fever Virus. Outbreaks were reported in Micronesia in 2007 and in Brazil in 2015, confirming at least 13 autochthonous infections. The Zika virus outbreak in Brazil in 2016 has gained world-wide attention, and has been linked to an increasing number of microcephaly cases. Clinically Zika virus can cause mild fever, rash, myalgia, arthralgia and headaches, with one in four infected individuals being asymptomatic. Due to similar symptoms Zika virus infected individuals can easily be mis-diagnosed as a dengue infection and vice-versa. In addition, Zika virus has been implicated in causing microcephaly through transmission in utero. There is no vaccine or specific treatment available for Zika virus.
Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) are an emerging vaccine technology. VLPs consist of protein shells comprising outer proteins specific to the virus in question. VLPs are more representative of how viral antigens are presented in vivo and while they are highly immunogenic they are non-infectious as they lack the core genetic material of the virus. Another important advantage of VLPs is that they more effectively activate key aspects of the immune response to achieve potent immune stimulation and to provide immunological memory. VLP-based vaccines have also shown to provide effective protection and are in current use for several diseases and in development for many others.
REFERENCES