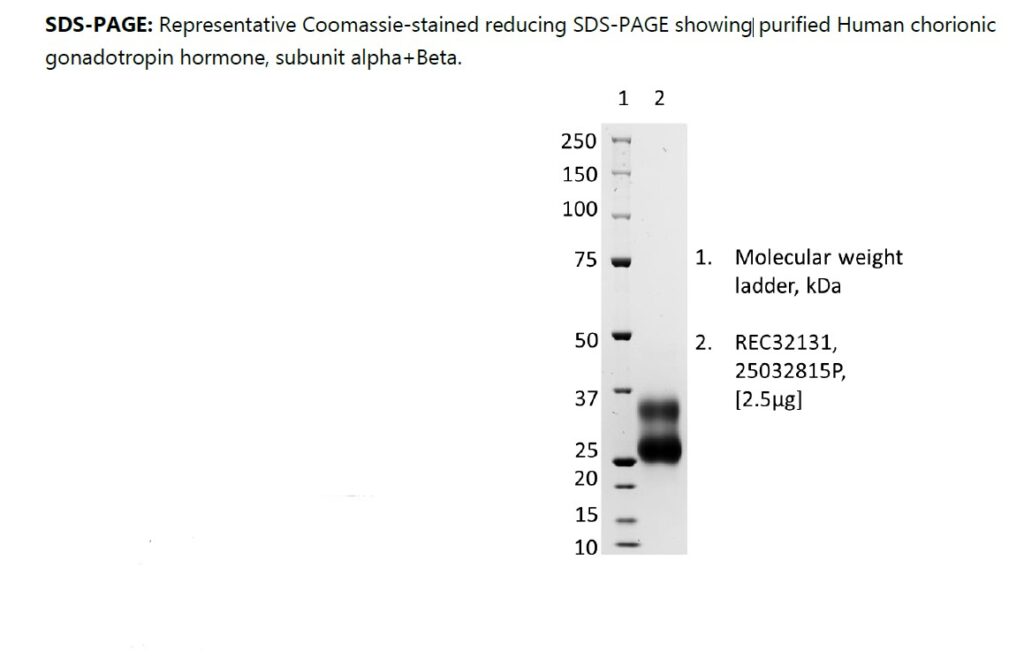
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (subunit alpha+beta), Recombinant
Price range: $164.30 through $3,839.69 excl. VAT
Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, subunits alpha and Beta, produced in HEK293 cells and purified by affinity chromatography and dialysis.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (subunit alpha+beta), Recombinant
Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, subunits alpha and Beta, produced in HEK293 cells and purified by affinity chromatography and dialysis.
PRODUCT DETAILS – Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (subunit alpha+beta), Recombinant
- Accession: P01215, P0DN87
- Tag: His-tag / 2xStrep-tag, C-Terminus
- Expressed and purified from HEK293 cells
- Presented as liquid in DPBS
- A sample of recombinant hCG diluted in a negative human plasma matrix to 0.5ug/ml returned a mean value 7837µIU/mL when tested using a Roche Cobas 6000 analyzer.
BACKGROUND
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a glycoprotein hormone primarily produced by placental trophoblast cells during pregnancy. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the corpus luteum and supporting progesterone production in early gestation. Structurally, hCG is a heterodimer composed of a common alpha-subunit and a unique beta-subunit, the latter conferring its specific biological activity (Fan et al., 2017)
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) was traditionally extracted from the urine of pregnant women (uhCG), but this approach faced challenges including large material requirements, inconsistent supply, contamination risks, and batch variability, leading to unpredictable patient responses. Recombinant hCG overcomes these issues by offering a highly pure, consistent, and contamination-free product, improving clinical outcomes in fertility treatments and serving as a reliable standard for calibrating diagnostic assays (Cole et al., 2004, Ludwig et al ., 2003).
REFERENCES
Fan, J., Wang, M., Wang, C., & Cao, Y. (2017). Advances in Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Detection Technologies: A Review. Bioanalysis, 9(19), 1509–1529.
Cole LA, Sutton JM, Higgins TN, Cembrowski GS. Between-method variation in human chorionic gonadotropin test results. Clin Chem. 2004 May;50(5):874-82.
Ludwig, M., Doody, K. J., & Doody, K. M. (2003). Use of recombinant human chorionic gonadotropin in ovulation induction. Fertility and Sterility, 79(5), 1051–1059.