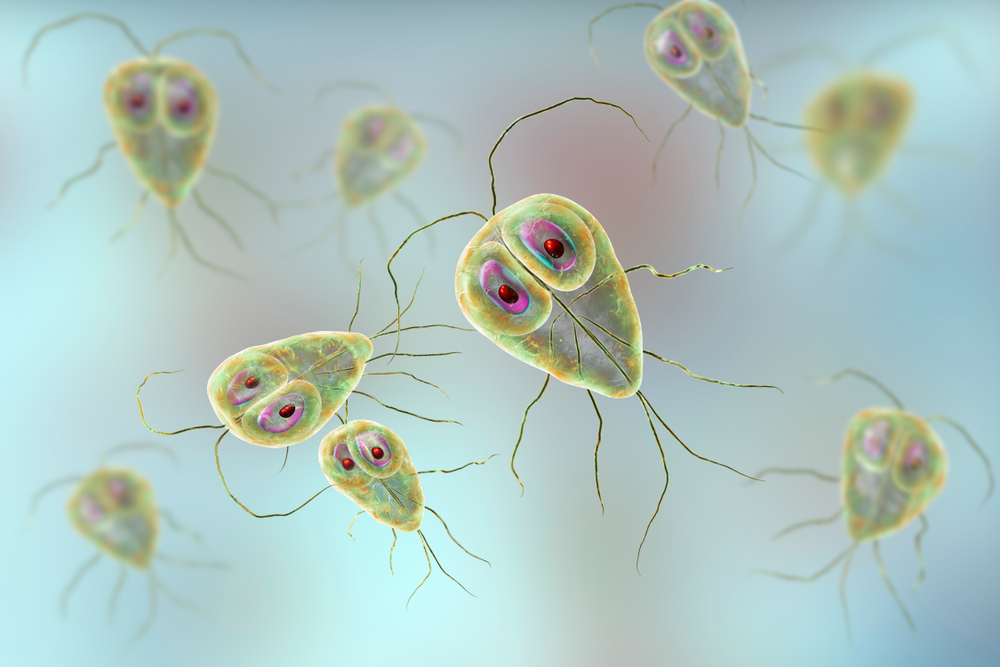
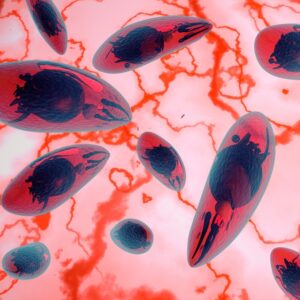
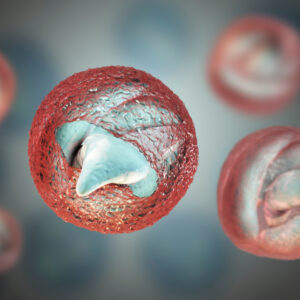
GIARDIA LAMBLIA CYSTS
Giardia lamblia cysts were purified from the faeces of experimentally infected gerbils using density gradient centrifugation and repeated washing. The Giardia Lamblia cysts have been heat inactivated.
PRODUCT DETAILS – GIARDIA LAMBLIA CYSTS
- Giardia lamblia cysts, strain H3.
- 2×10 to the 5 cysts (approx. 0.1 mg) and 1×10 to the 6 cysts (approx. 0.5 mg) available; where dry weight of 2×10 to the 6 cysts is estimated to be 1.0 mg.
- The product has been heat inactivated at 80ºC for 20 minutes. This exceeds the temperature required to completely inactivate Giardia cysts.
- Presented as liquid in in phosphate buffered saline pH 7.4.
- For use in assay development and as an immunogen for antibody generation.
BACKGROUND
Giardia and Cryptosporidium are both protozoan parasites that produce cysts, which can lead to gut borne infections Giardiasis and Cryptosporidiosis, respectively. Giardia lamblia (G. lamblia) is an anaerobic, flagellated eukaryotic protozoan, which is a member of the Hexamitidae family of protozoa. Giardia lamblia, also known as Giardia intestinalis or Giardia duodenalis, infects and colonises the small intestine of humans and mammals causing a globally common diarrheal disease known as giardiasis.
Giardia lamblia exists in two forms, as a dormant cyst that infects the small intestine and as a trophozoite, a vegetative form that excysts from the cyst. Trophozoites replicate within the intestine causing the symptoms associated with giardiasis. Both cysts and trophozoites are present in contaminated faeces but trophozoites do not survive for long periods in the environment. G. lamblia cysts are found in soil and water, and on surfaces contaminated by faeces from an infected individual. Giardiasis infection in humans occurs by transmission of dormant G.lamblia cysts via the faecal oral route or through ingestion of contaminated food and water (CDC). Intestinal protozoa are important etiological agents of diarrhea, particularly in children, yet the public health risk they pose is often neglected. Giardia infects approximately 200 million individuals worldwide, and causes acute diarrhea in children under 5 years.
REFERENCES
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Parasites-Giardia