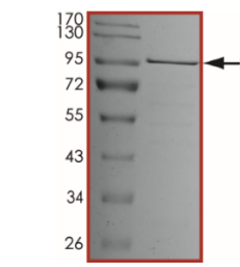
SDS-PAGE: The purity of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp was determined to be >85% by densitometry, approx. MW ~100 kDa.
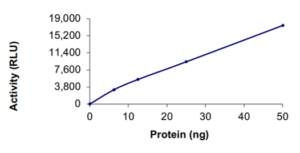
Activity: Determined by detection of pyrophosphate (PPi) generated during nascent strand synthesis by a chemiluminescent coupled assay method using ATP sulfurylase and luciferase.
SARS-COV-2 RNA-DEPENDANT RNA POLYMERASE (RdRp), ACTIVE
Recombinant full-length SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) was expressed in E. coli cells using a C-terminal His-tag and shown to be active in a chemiluminescent coupled assay. SARS-CoV-2, previously known as the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), causes the pandemic COVID-19 disease.
PRODUCT DETAILS – SARS-COV-2 RNA-DEPENDANT RNA POLYMERASE (RdRp), ACTIVE
- Recombinant full-length SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp).
- Expressed in E. coli cells with an C-terminal His-tag and >85% purity.
- Presented as liquid in 50mM sodium phosphate, pH7.5, 300mM NaCl, 150mM imidazole, 1mM DTT, 10% glycerol.
- Activity determined by detection of pyrophosphate (PPi) generated during nascent strand synthesis by a chemiluminescent coupled assay method using ATP sulfurylase and luciferase
BACKGROUND
In December 2019 a novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), formerly known as the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) was identified in Wuhan, China, causing a world-wide pandemic. Three coronaviruses, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 have been identified as being a highly pathogenic for humans, and there is currently no effective antiviral treatment. Therefore, studies are focused on rapid development of vaccines and antiviral drugs to prevent and treat coronavirus infection. There are several potential strategies to pharmacologically fight against the disease (COVID-19), including vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, oligonucleotide-based therapies, peptides, interferon therapies, and small-molecule drugs (Dömling & Gao, 2020). RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is an enzyme that is crucial to life cycle of RNA viruses including coronaviruses (Subissi et al., 2014). RdRp catalyzes the synthesis of viral RNA, thereby playing a central role in the replication and transcription cycle of COVID-19 viruses, possibly in complex with nsp7 and nsp8 (Gao et al., 2020). Therefore, RdRp is a prime target for nucleotide analog antiviral inhibitors, such as remedesivir, for development of new antiviral therapeutics (Wang et al., 2020).
REFERENCES
- Dömling A, Gao L. Chemistry and Biology of SARS-CoV-2. Chem. 2020;6(6):1283-1295.
- Gao Y, et al: Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science. 2020, 368: 779-782.
- Subissi L, et al: One severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus protein complex integrates processive RNA polymerase and exonuclease activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2014, 111: E3900–E3909.
- Wang M, et al: Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30:269–271.