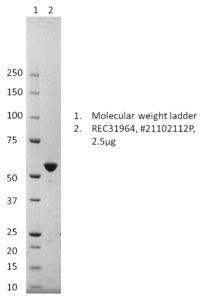
SDS-PAGE: Representative Coomassie-stained reducing SDS-PAGE showing purified IAV G4 EA nucleoprotein.
Influenza A G4 EA (H1N1) Nucleoprotein (NP), His-Tag
Price range: $512.90 through $1,948.60 excl. VAT
Influenza A G4 EA (H1N1) nucleoprotein (NP) is a recombinant influenza A swine G4 reassortant nucleoprotein, expressed and purified to high purity from Escherichia coli.
INFLUENZA A G4 EA (H1N1)] NUCLEOPROTEIN (NP), HIS-TAG
Influenza A G4 EA (H1N1) nucleoprotein (NP) is a recombinant influenza A swine G4 reassortant nucleoprotein, expressed and purified from Escherichia coli.
PRODUCT DETAILS – INFLUENZA A G4 EA (H1N1)] NUCLEOPROTEIN (NP), HIS-TAG
- Influenza A G4 EA (H1N1) nucleoprotein (NP), strain A/swine/Laiwu/16/2017 (Accession: AZB53091.1)
- Protein is expressed and purified from Escherichia coli to >90% purity
- Presented in 50mM Tris-HCl, 400mM NaCl pH8.0.
BACKGROUND
Studies conducted between 2011 and 2018 in China, and based on surveillance data in pigs, have identified an emerging genotype 4 (G4) reassortant Eurasian avian-like (EA) A(H1N1) swine influenza virus that contains internal genes from the human A(H1N1)pdm09 and North American triple-reassortant (TR) lineage-derived internal genes (Sun et al., 2020). When a single pig becomes infected with multiple influenza viruses the viruses can exchange genes by reassortment, generating new virus strains. The G4 is virtually reassorted by EA-H1N1, pdm/09 H1N1, and triple reassortment H1N1 containing internal elements from avian, human, and swine-origin influenza viruses. Several pandemics have been caused by these swine-origin influenza virus (Team NS-OIAVI, 2009). These viruses can replicate in human epithelial cells and spread through respiratory droplets between ferrets. Antisera against seasonal human A(H1N1)pdm09 virus showed poor reactivity with G4 viruses. Serosurveys also found that 10% (35/338) of swine farm workers were positive for this G4 EA A(H1N1) virus, with a higher proportion in people between 18 and 35 years of age (21%; 9/44) (Sun et al., 2020). These findings raise concern about the pandemic potential of these viruses, which are already able to replicate successfully in human tissue and transmit through droplets between ferrets, being a model for human-to-human transmission.
Swine influenza causes mainly mild disease in pigs and is not a disease that meets the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) criteria for disease notification (OIE, 2014). Although there are no surveillance programmes to monitor swine flu systematically on a global level, a joint OIE-FAO network of expertise on influenza, called OFFLU, supports international efforts to monitor, share biological material and data of animal influenza viruses for the development of human pandemic vaccines.
The Native Antigen Company has manufactured this G4 EA nucleoprotein to further enable the development of diagnostics and vaccines for pandemic preparedness.
REFERENCES
- Sun H, Xiao Y, Liu J, Wang D, Li F, Wang C, et al. Prevalent Eurasian avian-like H1N1 swine influenza virus with 2009 pandemic viral genes facilitating human infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2020:201921186.
- Team NS-OIAVI. Emergence of a Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus in Humans. New England Journal of Medicine. 2009;360(25):2605-15.
- World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). Terrestrial Animal Health Code (2014).

![Influenza A [A/Hong Kong/483/97 (H5N1)] Hemagglutinin (HA), His-Tag](https://thenativeantigencompany.com/wp-content/uploads/1970/01/shutterstock_1204546204-300x300.jpg)
![Influenza A [A/Hong Kong/45/2019 (H3N2)]](https://thenativeantigencompany.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Misc-Virus-122-300x300.jpg)