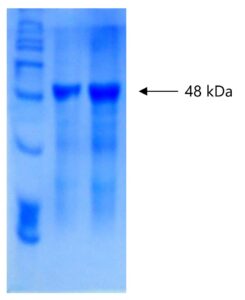
SDS-PAGE: Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE showing purified SARS-CoV-2 Omicron nucleoprotein.
SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.1.529/Omicron) Nucleoprotein, His-Tag (E. coli)
Price range: $697.88 through $2,659.10 excl. VAT
OMICRON VARIANT
SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.1.529/Omicron) nucleoprotein is a recombinant Omicron NP expressed and purified from E. coli. Compared to wild type SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein, Omicron nucleoprotein has the following mutations, P13L, ∆31-33, R203K, G204R. SARS-CoV-2, previously known as the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), causes the pandemic COVID-19 disease.
SARS-COV-2 (B.1.1.529/OMICRON) NUCLEOPROTEIN, HIS-TAG (E. COLI)
SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.1.529/Omicron) nucleoprotein is a recombinant Omicron NP expressed and purified from E. coli. Compared to wild type SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein, Omicron nucleoprotein has the following mutations, P13L, ∆31-33, R203K, G204R. SARS-CoV-2, previously known as the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), causes the pandemic COVID-19 disease.
PRODUCT DETAILS – SARS-COV-2 (B.1.1.529/OMICRON) NUCLEOPROTEIN, HIS-TAG (E. COLI)
- Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid phosphoprotein (B.1.1.529/Omicron).
- Expressed and purified from E. coli as full-length nucleoprotein, with a N-terminal 6xHis-tag.
- SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein (E. coli) is presented in PBS with 25mM K2CO3.
BACKGROUND
SARS-CoV-2 is a respiratory virus which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); it spreads primarily through contact with an infected person through respiratory droplets generated when a person coughs or sneezes, or through droplets of saliva or discharge from the nose. The incubation period is believed to range from 2-11 days. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 can cause mild symptoms including a runny nose, sore throat, cough, and fever. However, it can be more severe for some people and can lead to pneumonia or breathing difficulties. The elderly, and people with pre-existing medical conditions (such as, diabetes and heart disease) appear to be more vulnerable to becoming severely ill with the virus (WHO, 2020).
Coronaviruses encode five structural proteins in their genomes; namely, the Spike (S), Membrane (M), Envelope (E) glycoproteins, Hemagglutinin Esterase (HE) and Nucleoprotein (N), (Figure 2). All envelope proteins and N protein is present in all virions but HE is only present in some beta coronaviruses (Tok and Tatar, 2017). There are three main groups of coronaviruses: alpha, beta, and gamma. Nucleoproteins, also known as nucleocapsid proteins, are phosphoproteins that are capable of binding to helix and have flexible structure of viral genomic RNA. It plays an important role in virion structure, replication and transcription of coronaviruses, as it localizes in both the replication/ transcriptional region of the coronaviruses and the ERGIC region where the virus is collected. It packages the positive strand viral genome RNA into a helical ribonucleocapsid (RNP) and plays a fundamental role during virion assembly through its interactions with the viral genome and membrane protein M. It also plays an important role in enhancing the efficiency of subgenomic viral RNA transcription as well as viral replication. There is structural similarity between porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), a member of Arteriviridae, suggesting a common origin for Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae nucleoproteins (Yu et al., 2006).
South Africa reported the identification of a new SARS-CoV-2 variant, B.1.1.529, to the World Health Organization (WHO) on November 24, 2021. B.1.1.529 was first detected in specimens collected in Botswana and South Africa. On December 1, 2021, the first case attributed to B.1.1.529 was reported in the United States in a person who returned from travel to South Africa. The Omicron variant has since been detected in travel-related cases in an increasing number of European countries, as well as Australia, Brazil, Canada, Hong Kong, Israel, Japan, Nigeria, Norway, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. A few countries, including the United States, have reported cases in individuals without travel history to southern Africa.
On November 26, 2021, the Technical Advisory Group on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Evolution (TAG-VE) convened to assess B.1.1.529. The TAG-VE advised WHO that this variant should be designated as a Variant of Concern (VOC), and WHO designated B.1.1.529 as a VOC named Omicron. The European Center for Disease Prevention and Control also classified this variant as a VOC due to concerns regarding immune escape and potentially increased transmissibility compared to the Delta variant.
REFERENCES
- Tok and Tatar (2017). Structures and Functions of Coronavirus Proteins: Molecular Modeling of Viral Nucleoprotein -.International Journal of Virology & Infectious Diseases. Vol 2, 1.
- Yu et al. (2006). Crystal Structure of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein Dimerization Domain Reveals Evolutionary Linkage between Corona- and Arteriviridae. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, Vol. 281, No. 25, pp. 17134 –17139.
- Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), World health Organisation (WHO), 2020.