Western Blot: Western blot of recombinant P. multocida toxin (7.4 ng). Anti-PMT antibody was used at 1/1,000 dilution. As secondary antibody, HRP conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (ab 97051) was used at 1/20,000 dilution.
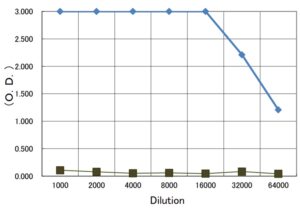
Indirect ELISA: Plate was coated with 0.2 μg of recombinant P. multocida toxin per well. 100 μl of anti-P. multocida toxin serum at the indicated dilution was added to each well and incubated. After washing, goat anti-rabbit-IgG conjugated with HRP was added as a secondary antibody. Colour was developed with TMB as substrate. Black boxes are data with pre-immune serum.
Rabbit Anti-Pasteurella Multocida Toxin Antibody
$649.73 excl. VAT
Anti-Pasteurella mulcosida toxin antibody, rabbit polyclonal.
RABBIT ANTI-PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA TOXIN ANTIBODY
Anti-Pasteurella mulcosida toxin antibody, rabbit polyclonal.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION – RABBIT ANTI-PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA TOXIN ANTIBODY
- Anti-Pasteurella mulcosida toxin antibody, rabbit polyclonal
- Affinity-purified with protein A/G mix from rabbit antiserum.
- Presented as liquid, in PBS, 50% glycerol.
- Applications include Western blotting (1/500-1/1,000 dilution), Dot blot (assay dependent), ELISA (assay dependent).
BACKGROUND
Pasteurella multocida is a frequent commensal of the respiratory tract of animals. As a facultative pathogen, it can lead to severe and economically important diseases, such as shipping fever in cattle, snuffles in rabbits, and fowl cholera in poultry and in humans is a zoonotic disease caused by scratches, bites, and saliva from pet animals such as cats and dogs (Harper et al., 2006; Wilkie et al., 2012).
P. multocida is a gram-negative coccobacillus. It is a non-motile, facultative anaerobe, and is generally penicillin-sensitive. There are five commonly isolated serogroups (A, B, D, E, and F), which are classified by the composition of the polysaccharide capsule. Most human infections are caused by serogroups A and D. P. multocida is the most common cause of soft tissue infection in humans following bites or scratches from dogs and cats. Pasteurella species are part of the normal flora of the mouth and upper respiratory tract of many animals, both wild and domestic. The animals with the highest rate of carriage are cats; dogs have the second-highest rate of carriage. One of the major virulence factors of P. multocida is the protein toxin PMT (P. multocida toxin), which is produced by serogroup D and some A strains. PMT is the causative agent to induce atrophic rhinitis in pigs, characterized by shortening and twisting of the snout due to the loss of nasal turbinate bones (Horiguchi, 2012).
PMT activates various heterotrimeric G proteins and many are substrates of the toxin. The 146-kDa toxin PMT comprises 1,285 amino acids (aa) (Orth & Aktories, 2012). Different domains of PMT are involved in cell uptake and intracellular action. The receptor binding and translocation domains are located in the N terminus (aa 1 to 574). Whereas the receptor binding domain has not been characterized in detail, two amphipathic helices, covering residues 402 to 457, are suggested to be involved in membrane insertion and translocation (Baldwin et al., 2004). So far, the cell surface receptor of PMT is not known (Brothers et al., 2011). PMT can be utilized as a transporter to carry a non-cell-permeating protein (DTa) as a fusion protein into the cytosol of host cells (Bergmann et al., 2013).
REFERENCES
- Baldwin MR, Lakey JH, Lax AJ. Identification and characterization of the Pasteurella multocida toxin translocation domain. Mol Microbiol. 2004 Oct;54(1):239-50.
- Brothers MC, Ho M, Maharjan R, Clemons NC, Bannai Y, Waites MA, Faulkner MJ, Kuhlenschmidt TB, Kuhlenschmidt MS, Blanke SR, Rienstra CM, Wilson BA. Membrane interaction of Pasteurella multocida toxin involves sphingomyelin. FEBS J. 2011 Dec;278(23):4633-48.
- Harper M, Boyce JD, Adler B. Pasteurella multocida pathogenesis: 125 years after Pasteur. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006 Dec;265(1):1-10.
- Horiguchi Y. Swine atrophic rhinitis caused by pasteurella multocida toxin and bordetella dermonecrotic toxin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;361:113-29.
- Orth JH, Aktories K. Molecular biology of Pasteurella multocida toxin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;361:73-92.
- Bergmann S, Jehle D, Schwan C, Orth JHC, Aktories K. Pasteurella multocida Toxin as a Transporter of Non-Cell-Permeating Proteins. Infect Immun. 2013 Jul; 81(7): 2459–2467.
- Wilkie IW, Harper M, Boyce JD, Adler B. Pasteurella multocida: diseases and pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;361:1-22.