Omicron Antigens Now Available
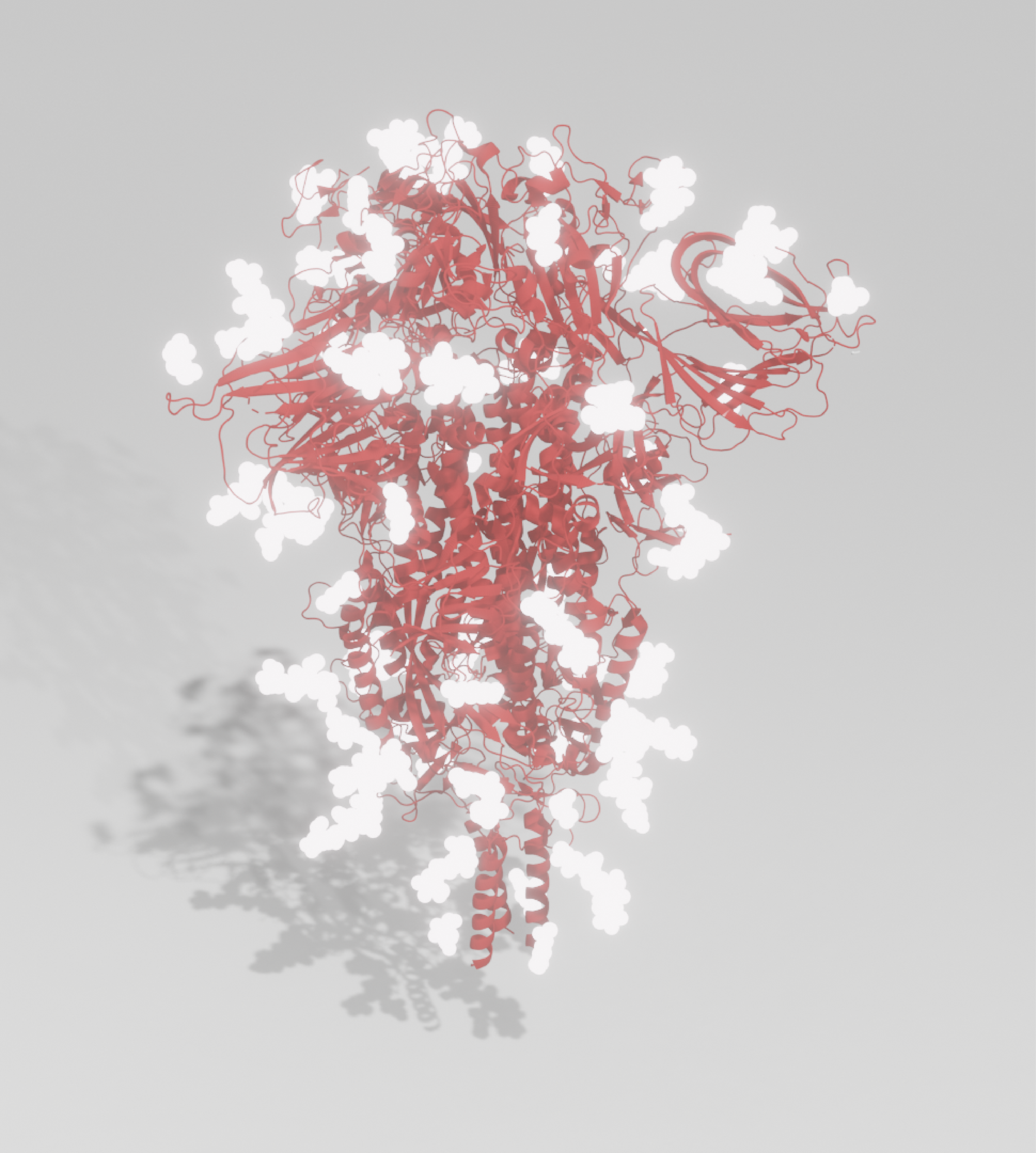
Produced from our VirtuE expression system, our Spike antigens exhibit full glycosylation and proper folding, ideal for developing high quality immunoassays and raising highly specific antibodies.
About the Omicron Variant
More recently, additional mutations in the BA.2 variant, variants BA.4 and BA.5, appear to have given transmissional advantages (Mahase 2022). BA.4 and BA.5 were first detected in South Africa in January and February 2022, respectively, where BA. 5 now accounts for more than half of the world’s cases, while BA. 4 just over one in ten (WHO Cronovirus Dashborad).
The World Health Organisation (WHO), in consultation with the Technical Group on Virus Evolution, have designated BA. 4 and BA. 5 as variants of concern (VOC) (Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants, WHO). The spike mutations of interest have been summarised in the table below (adapted from ECDC SARS-CoV-2 VOC Oct 2022).
| WHO Designation | Lineage | Spike mutations of interest (Spike mutation being monitored*) | Month & Year first detected |
| Omicron | BA. 2 | G142D, N211I, Δ212, V213G, G339D, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K | November 2021 |
| Omicron | BA. 4 | L452R, F486V, R493Q, R346X* | January 2022 |
| Omicron | BA. 5 | L452R, F486V, R493Q, R346X* | February 2022 |
Our Antigens
Our trimeric whole Spike antigen is stabilised as a pre-fusion trimer via six amino acid (HexaPro) changes in the S2 subunit, in addition to a GSAS mutation in the furin cleavage site and a His-Strep-tag at the C-terminus for ease of purification.
Our Spike S1 antigen includes residues 1-674 of the full Spike sequence and a C-terminal sheep Fc-tag for ease of purification.
Our Spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) antigen includes residues 319-542 of the full Spike sequence and a C-terminal His-tag for ease of purification.
Our Spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) antigen includes residues 23-245 (NCBI URX31554.1) of the full Spike sequence and a C-terminal His-tag for ease of purification.
Produced from our VirtuE expression system, our Spike antigens exhibit full glycosylation and proper folding, ideal for developing high quality immunoassays and raising highly specific antibodies.
For more information on these products, get in touch with a member of our team.
| Antigen | Mutations in Reference to Wuha-Hu-1 Wild-Type |
|
Whole Spike |
A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498RN501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| Spike S1 (REC32006) |
A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y |
| Spike RBD (REC32007) |
G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| Spike BA.5 (REC32036) |
G339D, S371F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, L452R, S477N, T478K, E484A, F486V, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
Get in touch
